Similarities to California?
 California is at the edge of two large underground plates. An earthquake in California is like hitting a bass drum on its edge: It doesn't really travel far. Missouri is in the middle of a plate. Seismic activity in Missouri is more like hitting the bass drum in the middle: It can resonate to Boston.
California is at the edge of two large underground plates. An earthquake in California is like hitting a bass drum on its edge: It doesn't really travel far. Missouri is in the middle of a plate. Seismic activity in Missouri is more like hitting the bass drum in the middle: It can resonate to Boston.
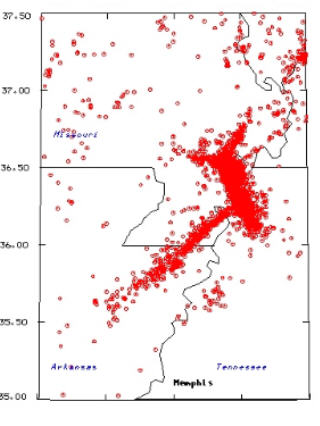
The 1811-12 New Madrid quakes were felt over more than 2 million square miles. By contrast, the 1906 earthquake in San Francisco, California, was felt over 60,000 square miles.
Gary Patterson, a geologist and information services director for the Center for Earthquake and Research Information in Memphis, said the incredible distance the quakes reached was largely due to the cold, solid rocks [tectonic plate] "that make this continent float," a different environment from the plate boundaries on the coast. More from Gary
"On the boundaries [like California], the [deep underground] rock is hot, molten and broken up," he said. The solid rock carries the movement farther from the epicenter.
A similarity between Missouri and California is that marshy low ground amplifies the shaking.
- Southern San Andreas ready to rumble - June 2006
- Map of California faults
- Great graphic of Bay area faults - USA Today
- Question is 'when' - USA Today Apr 2006
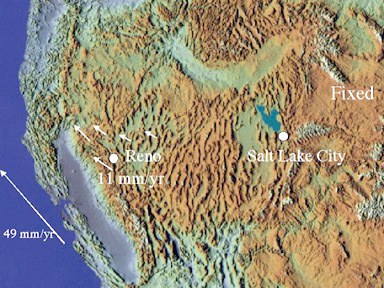 |
If 6 mm/year movement is serious, note the slip just off San Francisco Bay. Click the pic for description of what causes quakes. |
California (pronounce it like Arnold would) Sand and tectonic plates
This map illustrates the biggest problems of the 1989 San Francisco earthquake came in populated areas built on sand, miles from the epicenter.
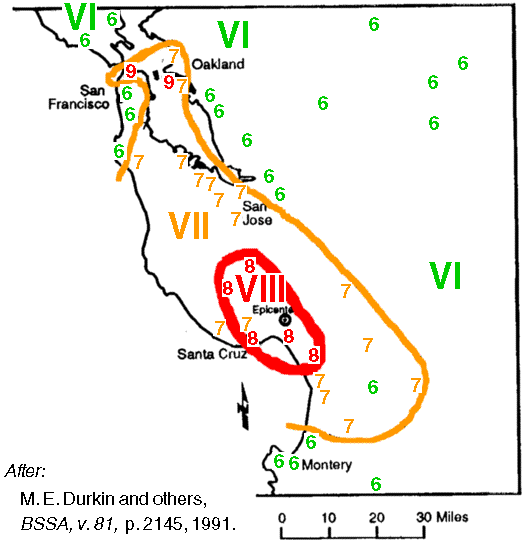 |
See the intensity level 9's near San Francisco? The left 9 marks the expensive Marina district, near the Golden Gate Bridge. The intensity was stronger there than at its epicenter, in the mountains 63 miles to the south. |
| 1989 Loma Prietra quake, Mercalli scale intensities |
|---|
Here's what a tourism website says about the picturesque Marina district's sandy soil.
This northernmost edge of San Francisco did not always teem with energy. When Juan Bautista de Anza claimed the area for Spain in 1776, it was a vast expanse of sand dunes, marshes, and willow forests. More than a century later, wanting to show that it had recovered from the catastrophes of 1906, the city filled 635 acres of wetlands with earthquake rubble on which to set the stage for the 1915 Panama-Pacific International Exposition.
Mercalli intensity numbers (1-12) show how a quake is felt, and can vary by location while a quake will have only one magnitude.
In the next 30 years, there is a greater than 70 percent chance of a major earthquake near San Francisco. Loma Prieta 1989 was not the "big one".(sfgate.com, Feb 21 2003).
"the USGS estimates that the chances of a major quake hitting the San Francisco Bay Area and Southern California are 67% and 60%, respectively." (Business Week Apr 18 2006)
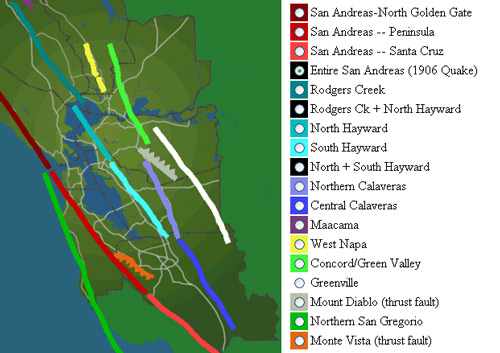 |
San Francisco has its faults. |
Tectonic plates meet in California. The Pacific Plate on which Los Angeles sits is moving slowly northwestward relative to the North American Plate on which San Francisco sits.
Two inches a year!
The map below comes from USGS, and shows movement at San Francisco. Click map for original.
Powered by Show-Me.net
